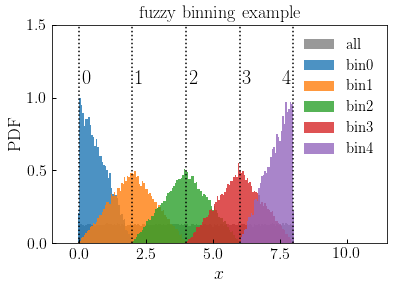
fuzzy_digitize¶
- halotools.utils.fuzzy_digitize(x, centroids, min_counts=2, seed=43)[source]¶
Function assigns each element of the input array
xto a centroid number.Centroid-assignment is probabilistic. When a point in
xis halfway between two centroids, it is equally likely to be assigned to the centroid to its left or right; when a point inxis coincident with a centroid, it will be assigned to that centroid with unit probability; assignment probability increases linearly as points approach a centroid.The
fuzzy_digitizefunction optionally enforces that elements of very sparsely populated bins are remapped to the nearest bin with more thanmin_countselements.- Parameters:
- xndarray
Numpy array of shape (npts, ) storing the values to be binned
- centroidsndarray
Numpy array of shape (num_centroids, ). The values of
centroidsmust strictly encompass the range of values spanned byxand must also be monotonically increasing.- min_countsint, optional
Minimum required number of elements assigned to each centroid. For those centroids not satisfying this requirement, all their elements will be reassigned to the nearest sufficiently populated centroid. Default is two.
- seedint, optional
Random number seed. Default is 43.
- Returns:
- centroid_indicesndarray
Numpy integer array of shape (npts, ) storing the index of the centroid to which elements of
xare assigned. All integer values ofcentroid_indiceswill lie in the closed interval [0, num_centroids-1].
Examples
>>> npts = int(1e5) >>> xmin, xmax = 0, 8 >>> x = np.random.uniform(xmin, xmax, npts) >>> epsilon, nbins = 0.001, 5 >>> xbin_edges = np.linspace(xmin-epsilon, xmax+epsilon, nbins) >>> centroid_indices = fuzzy_digitize(x, xbin_edges)